- Home
- >
- Material Bonding
- >
- UV Cure Adhesive For Acrylic
UV Cure Adhesive For Acrylic

In adhesive technology, UV cure adhesives for acrylic stand out as a revolutionary solution, providing unparalleled bonding prowess and efficiency. Harnessing the power of ultraviolet light, these adhesives offer rapid curing times and robust bonds, making them a go-to choice for various applications. From intricate crafts to industrial assemblies, UV cure adhesives for acrylic prove to be a versatile and reliable adhesive solution.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow does UV-cure adhesive for acrylic work?
UV-cure adhesives for acrylic, also known as ultraviolet (UV) light-curing adhesives, cure or harden when exposed to ultraviolet light. These adhesives are commonly used in bonding acrylic materials due to their fast curing time and strong bond.
Here’s a general overview of how UV-cure adhesives work for acrylic:
- Composition:UV-cure adhesives typically consist of monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, and other additives. Monomers and oligomers are the basic building blocks of the adhesive, while photoinitiators initiate the polymerization process when exposed to UV light.
- Application:The adhesive is applied to the surfaces of the acrylic parts that need to be bonded together. It’s essential to ensure the surfaces are clean and free from contaminants, as any foreign material could affect the bond.
- Exposure to UV Light:Once the adhesive is applied, the bonding process is initiated by exposing it to UV light. UV light is used to activate the photoinitiators in the adhesive. The light energy triggers a chemical reaction that starts the polymerization of the monomers and oligomers.
- Polymerization: Polymerization is the process by which small molecules (monomers) link together to form larger molecules (polymers). In the case of UV-cure adhesives, the polymerization process includes a three-dimensional network, creating a solid and durable bond between the acrylic surfaces.
- Curing Time:One of the significant advantages of UV-cure adhesives is their rapid curing time. The adhesive can harden within seconds to minutes, depending on the specific formulation, the UV light’s intensity, and the adhesive layer’s thickness.
- Strength and Clarity:UV-cure adhesives produce strong and clear bonds. The cured adhesive often has excellent transparency, making it suitable for applications where aesthetics are essential.
UV-cure adhesives are commonly used in industries such as electronics, optics, and medical devices, where fast and precise bonding of acrylic components is crucial. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper application and curing conditions ensures the best results.
What are the key advantages of using UV-cure adhesives?
UV-cure adhesives offer several key advantages, making them popular in various industries. Here are some of the main advantages:
Rapid Curing:
- One of the primary advantages of UV-cure adhesives is their quick curing time. When exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, these adhesives can cure in seconds or minutes, allowing for faster production.
Precise Control:
- UV-cure adhesives provide excellent control over the curing process. The curing reaction is initiated only when exposed to UV light, allowing for specific application and positioning of the adhesive before bonding.
No Solvents or Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):
- UV-cure adhesives are typically solvent-free, leading to a reduction in the emission of volatile organic compounds. This is advantageous for environmental and safety reasons, as well as for compliance with regulations.
Low Heat Generation:
- The curing process of UV-cure adhesives generates minimal heat. This benefits bonding heat-sensitive materials or components that elevated temperatures may damage during curing.
High Bond Strength:
- UV-cure adhesives can provide strong and durable bonds. The rapid curing process often results in a high crosslinking density, leading to robust adhesion between substrates.
Versatility in Substrate Compatibility:
- UV-cure adhesives are suitable for bonding a wide range of substrates, including glass, plastic, metal, and certain types of rubber. This versatility makes them applicable in various industries, such as electronics, medical devices, and automotive.
Enhanced Productivity:
- Due to their fast curing time and precise control, UV-cure adhesives contribute to increased production efficiency. Manufacturers can achieve higher throughput and faster assembly processes, improving overall productivity.
Improved Appearance:
- UV-cure adhesives often produce clear and transparent bonds, creating an aesthetically pleasing appearance. This is particularly important in applications where the visual appearance of the bonded materials is a crucial factor.
Cure On-Demand:
- UV-cure adhesives offer the advantage of on-demand curing. The curing process only begins when exposed to UV light, allowing operators to control when and where the bonding occurs.
Long Shelf Life:
- UV-cure adhesives typically have a long shelf life because the curing reaction only occurs when exposed to UV light. This feature ensures the adhesive remains stable and ready for use over an extended period.
Despite these advantages, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your application and the limitations of UV-cure adhesives, such as their sensitivity to UV light exposure and potential issues with bonding certain materials.
Can UV-cure adhesives bond other materials besides acrylic?
UV-cure adhesives are versatile and can bond substrates such as glass, metal, plastics, ceramics, and certain types of rubber. The key is that the related materials should be transparent or translucent to UV light, as the curing process relies on exposure to ultraviolet light to initiate the polymerization reaction.
Here are some common materials that can be bonded using UV-cure adhesives:
- Glass:UV-cure adhesives work well on glass surfaces.
- Metal:Many metals are suitable for bonding with UV-cure adhesives.
- Plastics:Different plastics, including polycarbonate, PVC, and others, can be bonded using UV adhesives.
- Ceramics:UV-cure adhesives can bond various ceramic materials.
- Certain Rubbers:Some rubber materials, especially those that are transparent or translucent to UV light, can be connected with UV-cure adhesives.
- Wood:UV-cure adhesives can also bond wood in specific applications.
It’s important to note that the bonding success depends on the specific formulation of the UV-cure adhesive and the compatibility with the bonded materials. Additionally, surface preparation, cleanliness, and proper curing conditions are crucial for achieving solid and durable bonds. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific UV-cure adhesive and the materials you are bonding.
Are UV-cure adhesives environmentally friendly?
UV-cure adhesives can be considered more environmentally friendly than traditional adhesive options. However, it’s important to note that the environmental impact of any adhesive depends on various factors, including its specific formulation, usage, and disposal.
Advantages of UV-cure adhesives in terms of environmental friendliness include:
- Low VOC Emissions:UV-cure adhesives often have low or zero volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. VOCs can contribute to air pollution and have adverse health effects.
- Energy Efficiency:The curing process of UV adhesives is relatively quick, requiring less energy than other curing methods. This can contribute to energy savings and a lower overall environmental footprint.
- Reduced Waste:UV adhesives typically cure on demand when exposed to UV light. This allows for precise application, reducing the likelihood of excess material being used and wasted.
- Solvent-Free:Many UV-cure adhesives are solvent-free, eliminating the need for harmful solvents that can adversely affect the environment.
- Long Shelf Life:UV adhesives often have a longer shelf life than other adhesives, reducing the likelihood of product spoilage and waste.
However, it’s crucial to consider the following factors:
- Raw Materials:The environmental impact depends on the materials used to formulate UV adhesives. Assessing the entire life cycle of the adhesive, from raw material extraction to disposal, is essential.
- Waste Disposal:While UV adhesives may be more environmentally friendly, it’s essential to consider properly disposing of cured and uncured residues. Some UV adhesives may contain components that could be challenging to dispose of in an environmentally friendly manner.
- Energy Source:The environmental impact of UV adhesives can also be influenced by the energy source used for curing. If the UV curing process relies on non-renewable energy, it may have a higher environmental impact.
To make an informed decision about the environmental friendliness of a specific UV-cure adhesive, it’s advisable to review the product’s Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), consult with the manufacturer, and consider the particular application and environmental regulations in your region.
What industries commonly utilize UV cure adhesive for acrylic?
UV cure adhesives are commonly used in various industries for bonding acrylic and other substrates due to their quick curing time and strong bond. Some sectors that frequently utilize UV cure adhesives for acrylic include:
- Electronics:UV cure adhesives assemble electronic components, such as bonding acrylic display screens, touch panels, and other electronic devices.
- Medical Devices:The medical industry often employs acrylic for various applications and UV cure adhesives are used to bond and assemble components in medical devices.
- Automotive:UV cure adhesives are used in the automotive industry to connect acrylic components in interior and exterior applications, such as instrument panels, displays, and lighting.
- Optical:Acrylic is commonly used in optical applications, and UV cure adhesives are utilized to assemble lenses, displays, and other optical components.
- Aerospace:UV cure adhesives find applications in the aerospace industry for bonding acrylic components in aircraft interiors, cockpit displays, and other aerospace-related applications.
- Signage and Display:Acrylic is a popular material for signage and displays. UV cure adhesives bond and assemble various acrylic components in the signage and display industry.
- Construction:UV cure adhesives are used in the construction industry for connecting acrylic materials in architectural applications, such as connecting acrylic panels for windows or decorative elements.
- Packaging:UV cure adhesives are used in the packaging industry to bond acrylic components in packaging materials and containers.
- DIY and Home Improvement:UV cure adhesives are also used by consumers for DIY projects and home improvement tasks involving acrylic bonding.
UV cure adhesives offer advantages such as rapid curing, low heat generation, and bonding transparent materials like acrylic without leaving visible residue. As a result, these adhesives are widely adopted in industries where fast and reliable bonding of acrylic components is essential.
How fast is the curing process with UV adhesives?
The curing process of UV (ultraviolet) adhesives is generally very fast compared to traditional adhesives that rely on evaporation or chemical reactions—UV adhesives cure when exposed to ultraviolet light, typically 200 to 400 nanometers. The curing time depends on various factors, such as the UV light’s intensity, the adhesive layer’s thickness, and the adhesive’s specific formulation.

In many cases, UV adhesives can cure in seconds to a few minutes. This rapid curing time makes them suitable for applications where quick bonding is essential, such as in the electronics industry for bonding components, medical device manufacturing, and various assembly processes.
It’s important to note that while the curing process is fast, proper equipment and conditions are necessary to ensure effective curing. Adequate exposure to UV light and consideration of factors like the type of bonded substrates is crucial to achieving optimal bond strength and performance. Additionally, the compatibility of the adhesive with the materials being bonded should be considered when choosing a UV adhesive for a specific application.
Are UV-cure adhesives resistant to environmental factors?
UV-cure adhesives can offer good resistance to environmental factors, but their specific performance depends on the formulation and intended use. Generally, UV-cure adhesives exhibit several characteristics that contribute to their resistance to environmental factors:
- Chemical Resistance:UV-cure adhesives can be formulated to resist exposure to various chemicals, solvents, and oils. This makes them suitable for applications where chemical exposure is a concern.
- Temperature Resistance:UV-cure adhesives can have a high-temperature resistance, making them ideal for applications where the bonded materials will be exposed to elevated temperatures.
- Moisture Resistance:Some UV-cure adhesives offer good resistance to moisture and humidity. This can be important in applications where the bonded materials may be exposed to environmental conditions that could cause other adhesives to degrade.
- UV Resistance:UV-cure adhesives cure and harden when exposed to ultraviolet light. Once cured, they often exhibit excellent resistance to UV radiation, preventing degradation from prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Durability:UV-cured adhesives can provide a durable bond, contributing to their resistance to environmental factors. The cured adhesive is typically rigid and resilient.
- Fast Cure Time:The fast curing nature of UV adhesives can be an advantage in applications where quick bonding and assembly are necessary, reducing the time materials are exposed to environmental factors before the adhesive is fully cured.
Despite these advantages, it’s crucial to note that the specific resistance of a UV-cure adhesive depends on the formulation and the intended application. It’s always recommended to consult the manufacturer’s technical data sheets and guidelines to ensure that the adhesive suits your application’s specific environmental conditions and materials. Testing under simulated or actual end-use conditions is often the best way to verify the adhesive’s performance in a particular environment.
Can UV-cure adhesives withstand temperature fluctuations?
UV-cure adhesives are known for providing fast and efficient bonding in various applications. However, the ability of UV-cure adhesives to withstand temperature fluctuations depends on the specific formulation of the adhesive and the intended application.
In general, UV-cure adhesives can exhibit good temperature resistance. Still, their performance may vary based on the type of polymer used, the curing process, and the environmental conditions they are exposed to. Some UV-cure adhesives are designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for applications where temperature fluctuations are typical.
It’s essential to consult the technical data sheet or product specifications provided by the adhesive manufacturer for detailed information on the temperature resistance of a specific UV-cure adhesive. Manufacturers often explain the temperature range within which the adhesive can maintain its bond strength and other mechanical properties.
If your application involves extreme temperature variations or specific temperature requirements, it’s advisable to choose an adhesive that is explicitly formulated and tested for those conditions. Additionally, consider factors such as the bonded substrate materials, exposure to chemicals, and any other environmental requirements that may affect the adhesive’s performance.
While UV-cure adhesives generally offer good temperature resistance, selecting the proper formulation based on your specific application and environmental demands is crucial. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and test the adhesive under the expected operating conditions to ensure optimal performance.
Are there specific safety considerations when using UV-cure adhesives?
UV-cure or ultraviolet light-cure adhesives are commonly used in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and optics. Here are some essential safety considerations:
- UV Exposure:UV-cure adhesives cure or harden when exposed to ultraviolet light. Prolonged exposure to UV light can be harmful to the skin and eyes. Using personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses, that provide UV protection is essential. Avoid direct exposure of the skin and eyes to the UV light source.
- Ventilation:Ensure proper ventilation in the working area to prevent the accumulation of fumes or vapors. Some UV-cure adhesives may release volatile compounds during curing, and adequate ventilation helps minimize exposure.
- Skin Contact:Avoid direct skin contact with uncured UV-cure adhesives. Use appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin irritation or sensitization. In case of skin contact, wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water.
- Eye Protection:UV light can cause damage to the eyes. Wear safety glasses or goggles with UV protection to shield your eyes from direct exposure. In case of accidental exposure, seek medical attention immediately.
- Material Compatibility:Ensure the UV-cure adhesive is compatible with the bonded materials. Some substrates may be sensitive to UV light or interfere with curing.
- Curing Time:Follow the recommended curing time provided by the adhesive manufacturer. Incomplete curing may result in reduced bond strength or other performance issues.
- Equipment Safety:When using UV light sources, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safely using equipment. Check that the equipment is in good working condition and avoid modifications that compromise safety.
- Storage:Store UV-cure adhesives according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, including temperature and humidity. Improper storage can affect the performance of the adhesive.
- Emergency Procedures:Be familiar with emergency procedures in case of accidental exposure, spills, or other incidents. Have access to emergency eye wash stations and safety showers in the vicinity.
- Training:Ensure that personnel working with UV-cure adhesives are adequately trained on the potential hazards, proper handling procedures, and the use of protective equipment.
Always refer to the specific safety data sheet (SDS) provided by the adhesive manufacturer for detailed information on safety precautions, handling, and emergency procedures related to the particular UV-cure adhesive you are using.
What distinguishes UV-cure adhesives from traditional bonding methods?
UV-cure adhesives differ from traditional bonding methods regarding their curing mechanism and application process. Here are some key distinctions:
Curing Mechanism:
- UV-Cure Adhesives:These adhesives cure when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. UV radiation initiates The curing process, which activates photoinitiators in the adhesive, leading to a rapid polymerization reaction. This results in a quick and efficient bond formation.
- Traditional Bonding Methods:Traditional adhesives often rely on physical or chemical processes for curing. Standard methods include air drying, solvent evaporation, heat curing, or chemical reactions between components. These processes may take longer compared to rapid UV curing.
Curing Time:
- UV-Cure Adhesives:UV-cure adhesives typically cure quickly, often within seconds to minutes. The fast curing time is advantageous for high-speed production processes.
- Traditional Bonding Methods:Traditional adhesives may require longer curing times, ranging from minutes to hours, depending on the type of adhesive and the curing conditions.
Controlled Curing:
- UV-Cure Adhesives:UV curing provides better control over curing since it only initiates when exposed to UV light. This allows for precise positioning and alignment of the bonded components before fixing.
- Traditional Bonding Methods:Some adhesives may require careful control of environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. The curing process may be less controllable compared to UV-cure adhesives.
Bond Strength:
- UV-Cure Adhesives:UV-cured bonds can exhibit high strength, providing excellent adhesion and cohesion properties. The quick curing process can result in strong and durable bonds.
- Traditional Bonding Methods:The bond strength of conventional adhesives can vary depending on the type of adhesive, substrate materials, and curing conditions. Some conventional adhesives may require longer curing times to achieve optimal strength.
Applicability to Heat-Sensitive Substrates:
- UV-Cure Adhesives:UV-cure adhesives are suitable for bonding heat-sensitive substrates since they do not rely on heat for curing.
- Traditional Bonding Methods:Some conventional adhesives may involve heat curing, which could limit their use with heat-sensitive materials.
Cleanliness and Environmental Considerations:
- UV-Cure Adhesives:UV-curing is a clean process usually involving minimal or no solvent emissions. This can be advantageous in terms of environmental and workplace safety.
- Traditional Bonding Methods:Traditional adhesives may include solvents, which can contribute to emissions and environmental concerns.
UV-cure adhesives offer rapid curing, precise control, and high bond strength, making them suitable for various applications, especially in industries where efficiency and quick turnaround are crucial. However, choosing between UV-cure adhesives and traditional bonding methods depends on specific application requirements and material considerations.
Can UV-cure adhesives be used for outdoor applications?
UV-cure adhesives are generally suitable for outdoor applications. Still, their performance depends on various factors, including the specific formulation of the adhesive and the environmental conditions in which they are used. UV-cure adhesives offer several advantages, such as rapid curing, high bond strength, and the ability to bond various substrates.
However, the long-term durability of UV-cure adhesives in outdoor environments may be influenced by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight, temperature fluctuations, moisture, and other environmental conditions. Some UV-cure adhesives are formulated with additives to enhance their resistance to outdoor exposure, while others may be better suited for indoor applications.
When selecting a UV-cure adhesive for outdoor use, it’s essential to consider the following:
- UV Stability:Ensure that the adhesive has good resistance to UV degradation. Some formulations are designed to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without significant performance loss.
- Weather Resistance:Check if the adhesive is formulated to resist the effects of rain, humidity, temperature extremes, and other weather conditions commonly encountered outdoors.
- Substrate Compatibility:Verify that the adhesive is compatible with the specific materials you intend to bond and any surface treatments or coatings on those materials.
- Temperature Range:Consider the expected temperature fluctuations in the outdoor environment and choose an adhesive to withstand those temperature extremes.
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations:Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for your specific adhesive product.
Testing the adhesive in representative outdoor conditions or consulting with the manufacturer for application-specific recommendations is advisable to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Some UV-cure adhesives may require additional protection, such as coatings or sealants, to enhance their resistance to outdoor exposure.
Do UV-cure adhesives affect the transparency of acrylic materials?
UV-cure adhesives can affect the transparency of acrylic materials depending on the specific adhesive and the acrylic formulation. UV-cure adhesives are designed to cure quickly when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, creating a solid bond. Several factors can influence the impact on transparency:
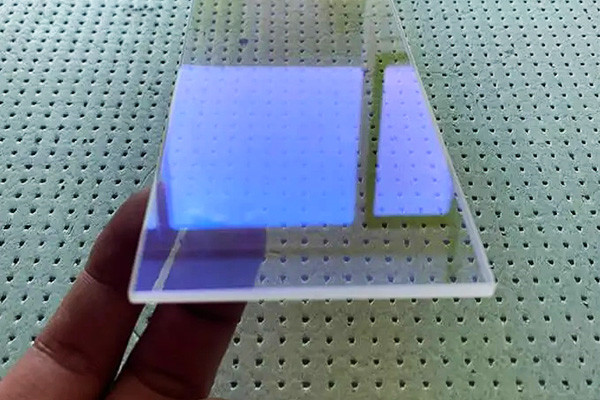
- Adhesive Formulation:Different UV-cure adhesives have different chemical formulations. Some adhesives may have components that can cause discoloration or affect the clarity of acrylic materials. Choosing an adhesive specifically designed for use with transparent materials like acrylic is essential.
- UV Light Intensity and Exposure Time:The curing process of UV-cure adhesives relies on exposure to UV light. If the UV light intensity or exposure time is too high, it may change the optical properties of acrylic, such as yellowing or hazing. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for UV light exposure.
- Acrylic Type:There are different types of acrylic materials with varying formulations. Some acrylics are more prone to yellowing or other changes when exposed to UV light. High-quality, UV-resistant acrylic materials are less likely to be affected.
- Testing:Before using any UV-cure adhesive on acrylic, conducting a small-scale test is advisable. Apply the adhesive to a small, inconspicuous area and cure it with UV light. Evaluate the transparency and appearance of the acrylic after curing to ensure compatibility.
- UV Stabilizers:Some acrylic materials may include UV stabilizers to protect against the effects of UV light. These stabilizers can help maintain transparency and prevent yellowing or other changes.
While UV-cure adhesives are generally suitable for bonding transparent materials like acrylic, choosing the right adhesive and following proper application procedures is crucial. Conducting small-scale tests and adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations can help ensure that the adhesive does not negatively impact the transparency of acrylic materials.
What is the shelf life of UV cure adhesive for acrylic?
The shelf life of UV cure adhesive for acrylic can vary depending on the specific product and its formulation. UV cure adhesives typically consist of monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, and other additives. Over time, these components can degrade, leading to a decrease in the adhesive’s performance.
UV cure adhesives often have a shelf life ranging from six months to a couple of years. It’s crucial to check the manufacturer’s guidelines and product documentation for precise information on the shelf life of a particular UV-cure adhesive.
Factors that can influence the shelf life of UV cure adhesives include:
- Storage Conditions:Adhesives are typically sensitive to temperature and light. According to the manufacturer’s recommendations, storing the adhesive in a cool, dark place can help extend its shelf life.
- Container Seal:Proper sealing of the adhesive container is essential to prevent air and moisture from affecting the adhesive’s properties. Make sure to reseal the container tightly after each use.
- Chemical Composition:Different formulations of UV cure adhesives may have varying shelf lives based on their chemical makeup. Some formulations may be more stable over time than others.
- Exposure to UV Light:Exposure to ambient light, especially UV light, can prematurely initiate the curing process in the adhesive. Ensure the adhesive is stored away from direct sunlight or other UV light sources.
Always refer to the product’s technical data sheet or contact the manufacturer for accurate and specific information regarding the shelf life of a particular UV-cure adhesive for acrylic. It may still be usable if the adhesive has surpassed its shelf life. Still, its performance might be compromised, and it’s advisable to perform tests to confirm its effectiveness before critical applications.
Are there variations in viscosity for different applications?
Viscosity can vary significantly depending on the application and the specific requirements of the process or product involved. Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow, and it is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the composition of the fluid.
Here are some examples of how viscosity variations can be significant in different applications:
Food and Beverage Industry:
- In the food industry, viscosity is crucial for the texture and mouthfeel of products like sauces, dressings, and beverages.
- Different food products may require different viscosities for proper processing and packaging.
Automotive Industry:
- Motor oils and lubricants need specific viscosity ranges to ensure proper engine function.
- Transmission, brake, and other automotive fluids also have specific viscosity requirements.
Paints and Coatings:
- Viscosity is critical in the formulation of paints and coatings. It affects how the product spreads, adheres, and dries.
- Different paints (e.g., primer, topcoat) may require different viscosities for optimal application.
Pharmaceuticals:
- Pharmaceuticals, including oral syrups and intravenous medications, must have carefully controlled viscosity for accurate dosing and administration.
Oil and Gas Industry:
- Crude oil and natural gas have varying viscosities depending on the specific reservoir characteristics. This affects the ease of extraction and transportation.
Cosmetics and Personal Care Products:
- Lotions, creams, shampoos, and other personal care products must have the correct viscosity for easy application and a pleasant user experience.
Adhesives and Sealants:
- Viscosity is vital in adhesive and sealant formulations to ensure proper bonding and sealing properties.
Chemical Processing:
- Chemical processes often require precise viscosity control to maintain efficient mixing, pumping, and reaction rates.
Biotechnology:
- In biotechnological applications, such as fermentation processes, the viscosity of culture media can impact the growth of microorganisms and the production of desired compounds.
Ink and Printing:
- Inks for printing applications need specific viscosities to ensure smooth printing processes and high-quality results.
These examples illustrate that different applications have specific viscosity requirements to achieve the desired performance, quality, and functionality. Manufacturers carefully tailor the viscosity of their products to meet these particular needs.
How do UV-cure adhesives enhance design possibilities?
UV-cure adhesives offer several advantages that enhance design possibilities in various industries. Here are some ways in which these adhesives contribute to design flexibility:
- Rapid Cure Time:UV-cure adhesives cure almost instantly when exposed to ultraviolet light. This rapid curing allows for faster production cycles, reducing manufacturing time. Designers can work with quicker assembly processes and achieve higher throughput.
- Precise Control:UV-curing provides precise control over the curing process. Designers can control the intensity and duration of UV exposure, allowing for accurate placement and bonding of components. This level of control is crucial for intricate and delicate designs.
- Reduced Heat Generation:Compared to traditional curing methods like heat or chemical reactions, UV-cure adhesives generate minimal heat during curing. This is especially beneficial for heat-sensitive materials and components, expanding the range of materials that can be bonded without causing damage.
- Bonding Diverse Materials:UV-cure adhesives are versatile and can connect a wide range of materials, including glass, plastic, metal, and ceramics. This versatility opens up new design possibilities by allowing for the assembly of dissimilar materials, creating innovative product designs.
- Improved Aesthetics:The clarity and transparency of many UV-cure adhesives make them suitable for bonding transparent or translucent materials without leaving visible residue. This enhances the aesthetic appeal of the final product, which is particularly important in industries such as electronics and optics.
- Low Volatility:UV-cure adhesives typically have low or no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to a safer working environment. This is important for designers who prioritize sustainability and environmental considerations.
- Customization and Flexibility:UV-cure adhesives come in various formulations with different properties, such as flexibility, toughness, or elasticity. This allows designers to select adhesives that match the specific requirements of their designs. Additionally, the adaptability of UV-curing systems enables the bonding of large or small surface areas.
- Automation Compatibility:The rapid curing nature of UV adhesives makes them well-suited for automation processes. Automated assembly lines can benefit from the efficiency and speed of UV-cure adhesives, contributing to higher production volumes and consistent quality.
UV-cure adhesives enhance design possibilities by offering fast curing times, precise control, compatibility with diverse materials, improved aesthetics, and customization options. These advantages contribute to more efficient and innovative design processes across various industries.
Do UV cure adhesives require specialized equipment for application?
UV-cure adhesives do require specialized equipment for application. The critical component in the curing process of UV adhesives is ultraviolet (UV) light. These adhesives contain photoinitiators that initiate a chemical reaction that causes the adhesive to cure and harden quickly when exposed to UV light.
Here are some critical components of the specialized equipment used in the application of UV-cure adhesives:
- UV Light Source:UV-cure adhesives require a UV light source to initiate curing. This light source is typically a UV lamp or LED lamp. The wavelength of the UV light is crucial, and it must match the absorption spectrum of the photoinitiators in the adhesive.
- Curing System:This includes the mechanism for delivering the UV light to the adhesive. The curing system may be handheld for spot curing or integrated into a conveyor system for continuous processing in manufacturing.
- Light Guide or Fiber Optic Cable:In some applications, a light guide or fiber optic cable delivers the UV light precisely to the adhesive bond area. This allows for more controlled and focused curing.
- Control System:A control system is often necessary to manage the intensity and duration of UV light exposure. This ensures that the adhesive cures properly without causing damage to the substrate or other materials involved.
- Safety Measures:UV light can be harmful to the eyes and skin. Therefore, safety measures such as protective eyewear and clothing are essential during application.
UV-cure adhesives are commonly used in industries requiring rapid curing and strong bonds, such as electronics, medical devices, and optical assemblies. The equipment used for applying UV-cure adhesives can vary depending on the application’s specific requirements. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for the adhesive and associated equipment is essential to achieve optimal results.
Can UV cure adhesives be used in medical device manufacturing?
UV (ultraviolet) cure adhesives are commonly used in medical device manufacturing. These adhesives offer several advantages that make them suitable for various applications in the medical industry. Some of the key benefits include:
- Rapid curing:UV cure adhesives cure quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, allowing for fast processing and increased production efficiency.
- Precise control:The curing process of UV adhesives can be easily controlled, enabling manufacturers to achieve special bonding with minimal heat generation.
- Minimal heat generation:UV cure adhesives generate minimal heat during curing, which is crucial for sensitive medical devices and materials that may be adversely affected by high temperatures.
- Bond strength:UV adhesives can provide strong and durable bonds, contributing to medical devices’ overall reliability and performance.
- Versatility:UV cure adhesives can bond many substrates, including plastics, glass, metals, and ceramics, making them suitable for diverse medical device applications.
- Biocompatibility:Many UV cure adhesives are available in formulations that meet biocompatibility standards, making them safe for use in medical devices that come into contact with the human body.
- Sterilization compatibility:UV-cured bonds often resist standard sterilization methods used in the medical industry, such as gamma irradiation and ethylene oxide.
It’s important to note that while UV cure adhesives offer many advantages, their selection should be based on the specific requirements of the medical device and the materials involved. Additionally, compliance with regulatory standards and biocompatibility testing is crucial when using adhesives to manufacture medical devices. Manufacturers should thoroughly assess the suitability of UV cure adhesives for their intended applications and ensure that the chosen materials meet industry regulations and standards.
What factors influence the bond strength of UV cure adhesives?
Like any adhesive system, the bond strength of UV-cured adhesives is influenced by various factors. Here are some key factors that can impact the bond strength of UV cure adhesives:
Substrate Type:
- The nature of the materials being bonded plays a crucial role. Different substrates have different surface energies and chemical compositions, affecting how well the adhesive can adhere.

Surface Preparation:
- Proper surface preparation is essential. Surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from contaminants like grease, oil, or dust. Some substrates may benefit from pre-treatment methods, like plasma treatment, to enhance adhesion.
Adhesive Formulation:
- The composition of the UV-cured adhesive itself is a significant factor. The choice of monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, and additives can affect the adhesive’s properties, including bond strength.
UV Exposure Parameters:
- The intensity and duration of UV exposure during the curing process influence the final bond strength. Proper curing is essential for achieving the optimal properties of the adhesive.
Adhesive Thickness:
- The thickness of the adhesive layer can impact the cure depth and, consequently, the bond strength. Inadequate curing through a thick coating may result in lower bond strength.
Curing Environment:
- Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, can affect curing. Some adhesives may be sensitive to variations in these parameters.
UV Light Source:
- The type and quality of the UV light source used for curing can influence the performance of UV-cured adhesives. The wavelength of the light and its compatibility with the adhesive formulation are crucial.
Post-Cure Conditions:
- In some cases, post-curing or additional heat curing may be required to achieve the desired bond strength. This step is essential for ensuring the adhesive has fully cured and reached its maximum strength.
Mechanical and Thermal Stress:
- The bond strength may be influenced by the mechanical and thermal stress the bonded materials will be subjected to in their intended application. Understanding these stress factors is crucial for selecting an adhesive with the appropriate strength.
Adhesive Compatibility:
- Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the specific application requirements, including any chemical exposure, environmental conditions, or temperature extremes it may encounter.
Quality of Substrate Surface:
- The condition of the substrate surface, such as roughness or porosity, can impact the bond strength. Some adhesives may be better suited to different surface textures.
It’s important to note that the interactions between these factors can be complex, and optimization may require experimentation and testing under specific application conditions. Manufacturers often provide guidelines for optimal usage and curing conditions for their UV-cured adhesive products.
Are there any limitations or challenges associated with UV cure adhesives?
Like any other material or technology, UV cure adhesives have certain limitations and challenges. Some of the fundamental limitations and challenges associated with UV cure adhesives include:
- Substrate Sensitivity:UV cure adhesives may not be suitable for all substrates. Some materials may not transmit UV light effectively, hindering the curing process. Opaque or UV-absorbing substrates may pose challenges in achieving proper cure depths.
- Depth of Cure:UV light has a limited penetration depth, so the adhesive may not cure effectively in shadowed areas or may be challenging to reach. This can be a limitation in bonding complex or three-dimensional structures.
- Light Intensity and Distance:The effectiveness of UV curing depends on the UV light’s intensity and the distance between the light source and the adhesive. Curing may be incomplete if the intensity is too low or the distance is too great, leading to compromised bond strength.
- Temperature Sensitivity:UV cure adhesives may be sensitive to temperature variations. Excessively high or low temperatures can affect the curing process and the overall performance of the adhesive.
- UV Light Absorption:Some materials and pigments may absorb UV light, reducing the energy available for curing. This can impact the speed and completeness of the curing process.
- Chemical Resistance:UV cure adhesives may not exhibit the same level of chemical resistance as some other adhesive technologies. Their performance in harsh chemical environments may be limited and unsuitable for specific applications.
- Cost of Equipment:UV curing requires specialized equipment, including UV light sources. The initial investment in this equipment can be relatively high, and maintenance costs should also be considered.
- Health and Safety Considerations:UV light can harm human eyes and skin. Adequate safety measures, including personal protective equipment, are necessary when working with UV-cure adhesives.
- Moisture Sensitivity:Some UV cure adhesives are sensitive to moisture, and exposure to high humidity conditions can interfere with curing. Proper storage and handling are essential to maintain adhesive performance.
- Limited Working Time:UV cure adhesives typically cure rapidly once exposed to UV light. This can be an advantage in specific applications, but it also means limited time for repositioning or adjusting parts after application.
Despite these limitations, UV cure adhesives offer many advantages, including rapid curing, reduced solvent emissions, and bonding a wide range of substrates. The choice of adhesive depends on the application’s specific requirements, and it’s essential to carefully consider both the benefits and limitations of UV-cure adhesives in a given context.
How can one choose the UV cure adhesive for a specific acrylic application?
Choosing the suitable UV cure adhesive for a specific acrylic application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance. Here are some key factors to consider:
Substrate Compatibility:
- Ensure that the UV cure adhesive is compatible with acrylic substrates. Some adhesives may work better on certain types of acrylic, so check the product specifications and test on a small, inconspicuous area.
Bond Strength Requirements:
- Evaluate the bond strength needed for your application. Different UV cure adhesives may have varying degrees of bond strength. Consider the stress, load, and environmental conditions the adhesive will face.
Viscosity and Gap Filling:
- Viscosity is crucial, as it determines how well the adhesive can flow and fill gaps. Lower viscosity may be preferable for tight bond lines, while thicker adhesives may be better for filling more significant gaps.
Curing Time:
- UV cure adhesives cure quickly under ultraviolet light, but the curing time can vary. Consider your application’s production speed and the time available for the curing process.
UV Light Source:
- The type of UV light used for curing can impact the adhesive’s performance. Ensure the adhesive is compatible with your UV light source or plan to use. Familiar UV light sources are UV-A, UV-B, or UV-C lamps.
Temperature Resistance:
- Consider the temperature conditions the adhesive will be exposed to during its service life. Some UV-cure adhesives may have better resistance to high or low temperatures.
Chemical Resistance:
- Assess the resistance of the adhesive to chemicals or environmental factors it might encounter. This is especially important if the acrylic application will be exposed to harsh chemicals or other potentially damaging substances.
Transparency and Appearance:
- If the appearance of the bonded acrylic is critical, choose an adhesive that dries or cures to a finish that meets your aesthetic requirements. Some adhesives have better transparency and minimal yellowing over time.
Ease of Application:
- Consider the ease of application and whether the adhesive requires special handling or equipment. Some UV-cure adhesives may have specific application requirements that need to be considered.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure the chosen UV cure adhesive complies with industry standards or regulations relevant to your application.
Cost Consideration:
- Compare the cost of different UV cure adhesives, considering performance, reliability, and the overall value they provide for your specific application.
Testing:
- Perform small-scale tests or trials before full-scale application to ensure that the chosen adhesive meets the particular requirements of your acrylic bonding application.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a UV cure adhesive that aligns with the needs and conditions of your acrylic application. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and technical data sheets for detailed information about each adhesive product.
Conclusion: A Beacon of Bonding Excellence
In conclusion, UV cure adhesive for acrylic emerges as a beacon of bonding excellence, illuminating the path toward efficient, durable, and visually appealing assemblies. Its rapid curing, environmental resilience, and versatility make it a standout choice across diverse industries. As technology advances, UV cure adhesives continue to redefine the boundaries of what is achievable in the world of bonding, providing solutions that meet the demands of modern design and manufacturing. Whether you’re in artistry or engineering, UV cure adhesives for acrylic offer a transformative approach to bonding, ushering in a new era of adhesive excellence.

DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

Flexible & Durable UV Optical Adhesive for Glass Bonding Applications
Flexible & Durable UV Optical Adhesive for Glass Bonding Applications In the landscape of modern manufacturing, from the sleek touchscreens of consumer electronics to the complex lens assemblies in medical devices and the expansive displays in the automotive industry, glass has emerged as a material of choice. Its optical clarity, scratch resistance, and premium feel

Low Yellowing & Fast Curing UV Liquid OCA Glue for Touch Screens
Low Yellowing & Fast Curing UV Liquid OCA Glue for Touch Screens The relentless pursuit of thinner, brighter, and more durable display technologies has placed immense pressure on the materials used in their assembly. Optical Clear Adhesives (OCAs) are critical components in modern touch screen modules, responsible for laminating the cover glass to the

Step-by-Step Guide: Achieving Flawless Display Lamination with UV LOCA Glue
Step-by-Step Guide: Achieving Flawless Display Lamination with UV LOCA Glue The pursuit of perfect visual clarity and seamless integration in modern displays—from smartphones and tablets to specialty instruments and high-end automotive consoles—has made Optical Clear Adhesive (OCA) lamination a critical process. While traditional dry OCAs dominate mass production, UV-curable Liquid Optically Clear Adhesive (UV LOCA)

Best Practices for Curing UV Acrylic Adhesives: Mastering Light Wavelength & Time
Best Practices for Curing UV Acrylic Adhesives: Mastering Light Wavelength & Time UV-curable acrylic adhesives have revolutionized assembly processes across industries—from medical devices and electronics to aerospace and automotive—offering rapid curing, superior performance, and solvent-free processing. However, the efficiency and final properties of the bond are critically dependent on two fundamental parameters: the wavelength

Which UV-Curable Adhesives Are Suitable for Medical Device Applications?
Which UV-Curable Adhesives Are Suitable for Medical Device Applications? The medical device industry operates at the intersection of precision, reliability, and stringent safety standards. Every component, from intricate catheters and biosensors to robust surgical tools and diagnostic equipment, must perform flawlessly under demanding conditions. Joining these components presents a unique challenge: achieving strong, hermetic,

High Transmittance (>99%) UV Optical Clear Adhesive for Display Lamination
High Transmittance (>99%) UV Optical Clear Adhesive for Display Lamination The Imperative for Optical Purity Modern display technology—from OLED smartphones to mini-LED TVs and automotive dashboards—is fundamentally about controlling light. Every interface between materials presents an opportunity for light loss through reflection, scattering, or absorption. In a complex display module, comprising a cover glass,











